30+ Alkane To Alkene Oxidation
Alkane To Alkene Oxidation. The reactions of alkenes are studied in this chapter: Alkenes undergo a number of reactions in which the c=c double bond is oxidized.

Alkenes react with percarboxylic acids and even hydrogen peroxide to yield epoxides: Because potassium permanganate, which is purple, is reduced to manganese. Alkenes can easily be oxidized by potassium permanganate and other oxidizing agents.
2019 toyota rav4 hybrid xle price 12 x 36 poster 2020 volvo s60 polestar aspirateur rowenta air force extreme 24v avis
Halohydrin Formation Alkene Reaction Mechanism YouTube
For example, when propane is oxidized, the heat of combustion is 688 kilocalories per mole. Compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen and single bonds This change of mechanism gives rise to the opposite regiochemistry. Oxidation with oso 4 • oso 4 is an effective oxidizing agent in the conversion of an alkene to a glycol or vicinal diol, a compound with —oh groups on adjacent carbons • oxidation of an alkene by oso 4 is syn stereoselective • note that oso 4 is both expensive and highly toxic

10.7 oxidation reactions of alkenes. For alkenes, several carbon oxidation levels are again possible. Alkenes react with percarboxylic acids and even hydrogen peroxide to yield epoxides: Alkenes react with ozone, leading to the scission of. The energy released when an alkane is completely oxidized is called the heat of combustion.

The energy released when an alkane is completely oxidized is called the heat of combustion. Synthesis of ketones by oxidation of alkenes. At cold temperatures with low concentrations of oxidizing reagents, alkenes tend to form glycols. Furthermore, both carbon atoms must be considered as part of the same alkene functional group. Methane monooxygenases, related enzymes, and their biomimetics chem rev.
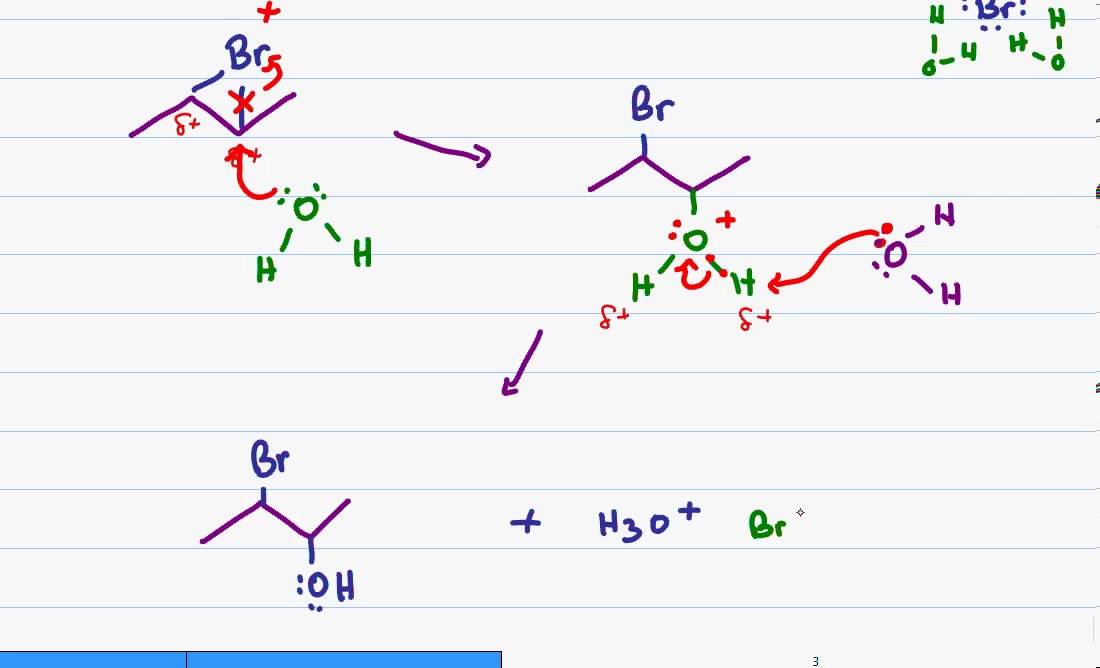
Alkenes can easily be oxidized by potassium permanganate and other oxidizing agents. Methane monooxygenases, related enzymes, and their biomimetics chem rev. Alkenes react better in oxidation reactions than alkynes because alkenes are less oxidized than alkynes. While the total oxidation level can go from −4 for ethylene (as the sum of the oxidation level of both carbon atoms in the.

Overall, therefore, there is no change to the oxidation state of the molecule. The energy released when an alkane is completely oxidized is called the heat of combustion. This video is the third topic of the thirteenth chapter (hydrocarbons). The free radical initiators change the mechanism of addition from electrophilic addition to free radical addition. Alkenes undergo a number of.

Alkenes can easily be oxidized by potassium permanganate and other oxidizing agents. Rch=ch 2 + rco 3 h → rchoch 2 + rco 2 h. Oxidation with oso 4 • oso 4 is an effective oxidizing agent in the conversion of an alkene to a glycol or vicinal diol, a compound with —oh groups on adjacent carbons • oxidation of.

Overall, therefore, there is no change to the oxidation state of the molecule. Methane monooxygenases, related enzymes, and their biomimetics chem rev. 10.7 oxidation reactions of alkenes. Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides. Some important oxidation reactions of alkanes are given below :

This is an overall oxidation. Alkanes can be oxidized to carbon dioxide and water via a free‐radical mechanism. Ii alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes hydrocarbon : Alkenes react with ozone, leading to the scission of. The product of these oxidations will depend on the reaction conditions.

Ii alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes hydrocarbon : Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides. Alkenes react better in oxidation reactions than alkynes because alkenes are less oxidized than alkynes. Overall, therefore, there is no change to the oxidation state of the molecule. While the total oxidation level can go from −4 for ethylene (as the sum of the oxidation level of both.