44+ Alkane Alkene Alkyne
Alkane Alkene Alkyne. 2.3 reactions of alkenes and alkynes ⇒ additions are the most common reactions using alkenes and alkynes addition to: 10) provide the structure of the major organic product(s) in the reaction below.

Structure and physical properties an unsaturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon containing at least one double or triple bond. The following examples show the 4 carbon alkane, alkene, and alkyne. The general chemical formula of alkanes is c n h 2n+2.
accessoires salle de bain de luxe aspirateur a main puissant boulanger aqualux 1200 manual anna faris em friends
The two things that have to be considered when predicting
Alkanes have the general chemical formula c n h 2n+2.the alkanes range in complexity from. Start studying alkanes and alkenes. The acidity is mainly due to the increase in the. Notice that the alkene only has one double bond and the alkyne only has one triple bond.

Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are all organic hydrocarbons. Many of these molecules are used in the production of other materials, such as plastics, but their main use is as a fuel source. For example, all the above unbranched alkenes shown had double bond at the first atom. The acidity is mainly due to the increase in the. Notice that the.

Alkanes are useful as fuels and alkenes are used to make chemicals such as plastic. Alkyl groups are alkanes lacking one hydrogen atom, thus having a vacant point to get attached to a carbon atom. The general chemical formula of alkanes is c n h 2n+2. Start studying alkanes and alkenes. Notice that the alkene only has one double bond.

C 2 h 4 + 3o 2 → 2co 2 + 2h 2 o. 10) provide the structure of the major organic product(s) in the reaction below. An organic molecule is one in which there is at least one atom of carbon, while a hydrocarbon is a molecule which only contain the atoms hydrogen and carbon. The general formula of.

Alkanes are useful as fuels and alkenes are used to make chemicals such as plastic. Reaction in which halogen is introduced into a molecule 3) hydration : Start studying alkanes and alkenes. The acidity is mainly due to the increase in the. C 2 h 4 + 3o 2 → 2co 2 + 2h 2 o.

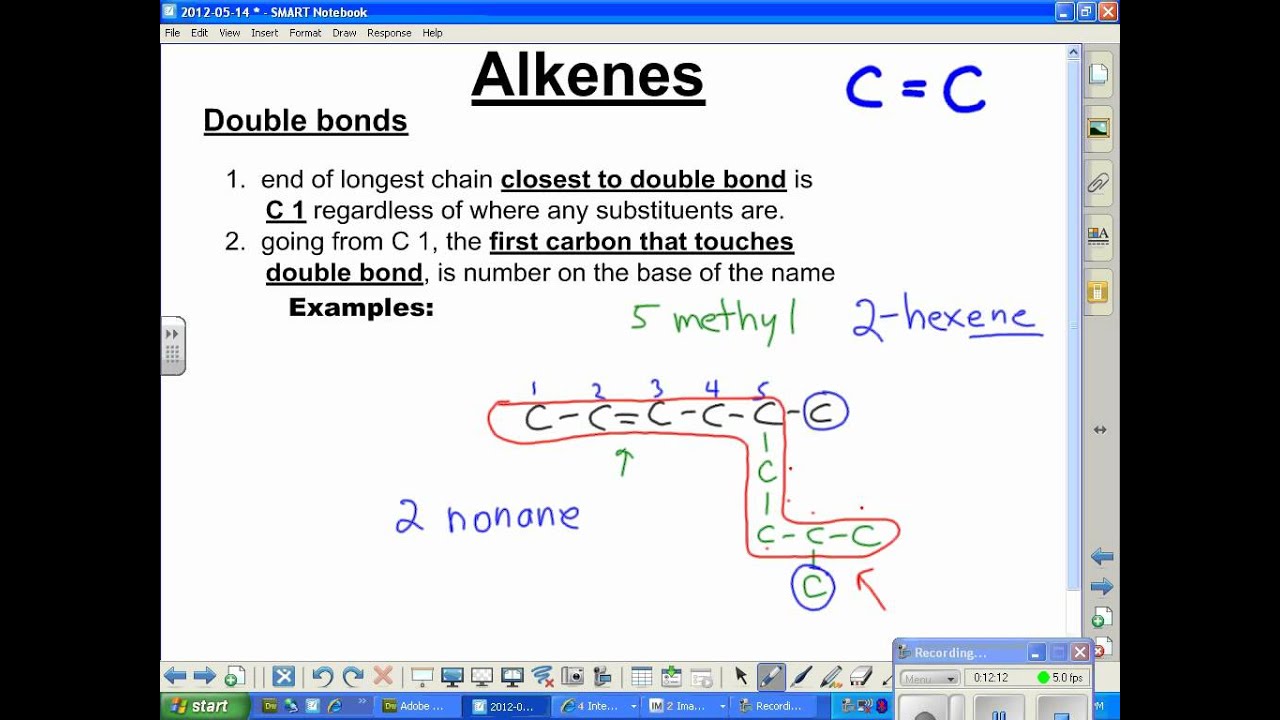
The general chemical formula of alkanes is c n h 2n+2. In alkenes, the carbon atom where the double bond is present represents the number with the alkene. An organic molecule is one in which there is at least one atom of carbon, while a hydrocarbon is a molecule which only contain the atoms hydrogen and carbon. Many of these.

Halogenation goes via free radical mechanism and thus lot of unwanted products + other isomers can be formed. Alkyne molecules have a triple bond (). Usually, alkanes are not considered functional groups; Many of these molecules are used in the production of other materials, such as plastics, but their main use is as a fuel source. Alkanes are useful as.
Reaction in which the elements of water (h and oh) are Alkyl groups are alkanes lacking one hydrogen atom, thus having a vacant point to get attached to a carbon atom. 1) addition of hydrogen halides 2) halogenation : We will review their nomenclature, and also learn about the vast possibility of reactions using alkenes and alkynes as starting materials..

Alkanes •only single bonds between carbon atoms. Usually, alkanes are not considered functional groups; The acidity is mainly due to the increase in the. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Structure and physical properties an unsaturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon containing at least one double or triple bond.